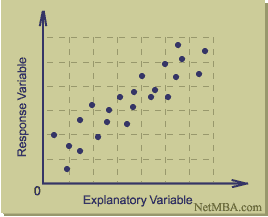
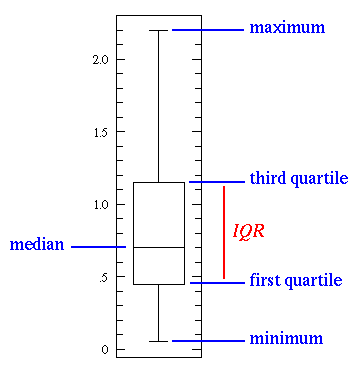
This is an image of a Correlation Matrix. A Correlation Matrix is a graphical representation of the correlation between two numeric variables.
This is an image of a Correlation Matrix. A Correlation Matrix is a graphical representation of the correlation between two numeric variables. This image is a Correlation Matrix of Strategic Objectives. The results from this matrix shows that firms focusing on creating shareholder value while also taking into account the needs of other stakeholders and employees, will achieve higher productivity. In summary, people matter and how they are managed and interact in the workplace is crucial to the productivity of any business. This matrix also shows that there are strong associations between stakeholder value, customer and market priorities, innovation and shareholder value.